Real Wages
View FREE Lessons!
Definition of Real Wages:
Real wages are nominal wages after being adjusted for inflation.
Detailed Explanation:
Real wages
(or income) are used when comparing a change in income over a period of time. “Real” adjusts any change in wages for inflation. These real values help economists decipher between changes resulting from fluctuating prices and changes resulting from other factors, such as shifting supply or demand curves. When the nominal wage increase is greater than inflation, there is a positive increase in the real wage. For example, assume you receive a pay increase of four percent, and the inflation rate is two percent, your real wage increase is two percent. Conversely, if your annual real wage increase is less than the inflation rate, you would not be able to purchase as large a bundle of goods and services as you could have purchased at the beginning of the year.
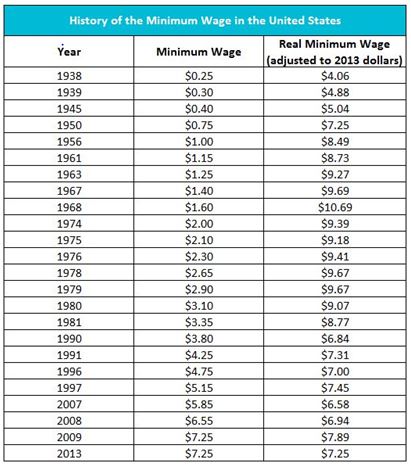
The table furnishes the history of the nominal and real minimum wages in the United States. Notice the difference in the minimum wage after being adjusted for inflation. Wages are adjusted to 2013 dollars.
Pew Research – Real Wages in the United States
Dig Deeper With These Free Lessons:
Inflation
Causes of Inflation
Gross Domestic Product – Measuring An Economy’s Performance
Business Cycles