Gross national product (GNP) is the market value of all final goods and services produced by the companies of a country in a specific period.
Goods and services produced by American companies would be included in the United States’ GNP regardless of where they were manufactured. BMW® automobiles produced in the United States would not be included in the American GNP, but they would be included in Germany’s GNP because BMW is a German company. Nike® shoes produced in China would be included in the US GNP because Nike is an American company. The formula for GNP is …
GNP = C + I + G + NX + OI – FI
C is consumer spending, I is private investment, G is government expenditures, NX equals net exports, OI is income residents earn outside the country, and FI equals income earned by foreign companies inside the country. Contrast GNP with the gross domestic product (GDP). Gross domestic product is the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a specified period of time. In this case, BMW ® automobiles produced in the United States would be included in GDP, but not GNP. Nike ® shoes produced in China would be not be included in the US GDP. They would be included in China’s GDP.
The formula for GDP is….
GDP = C + I + G + NX
Therefore, GNP is equal to…
GNP = GDP + OI – FI
GNP differs from GDP by adding in any income from a country’s foreign interests but subtracts domestic production by foreign companies. The diagram below illustrates the difference between GNP and GDP.
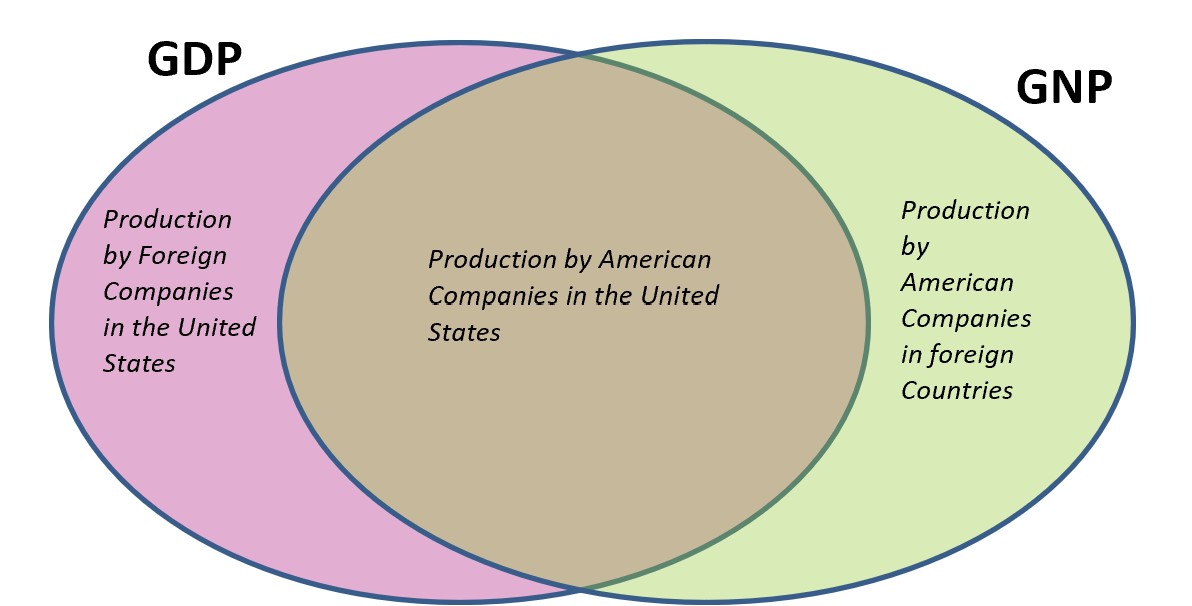
In countries with many foreign investors, the GDP is higher than GNP because it includes production within the borders. However, in countries that export a great deal of manufacturing, the GNP may be higher since it includes production outside a country’s borders. Most economists believe GDP is a better measure of a country’s production.
Gross Domestic Product – Measuring An Economy's Performance
Business Cycles
Production Possibility Frontier
Comparative Advantage and Specialization